Software Overview
3D scanning is only half of the equation
3D scanners collect half a million to three million points per second, so you can collect copious amounts of measurement data to represent the geometry of your parts with exceptional fidelity. Reliably taking advantage of all that information requires the right scan-native software.
This guide will explain the different free and professional software that you’ll need for your application. You can also take our 4 questions quiz below to find the right software for you!
Industry Applications
What are the different uses for 3D scanning?
Reverse Engineering
In solid modeling, an engineer creates a mechanical part out of solid primitives partially imitating the process of manufacturing (extruding, drilling). Solid modeling is parametric, meaning that the change of one parameter inevitably leads to the changes in the adjoining ones. The model has a parametric history displaying the design intent and the engineer can always go back to the previous stage to change it.
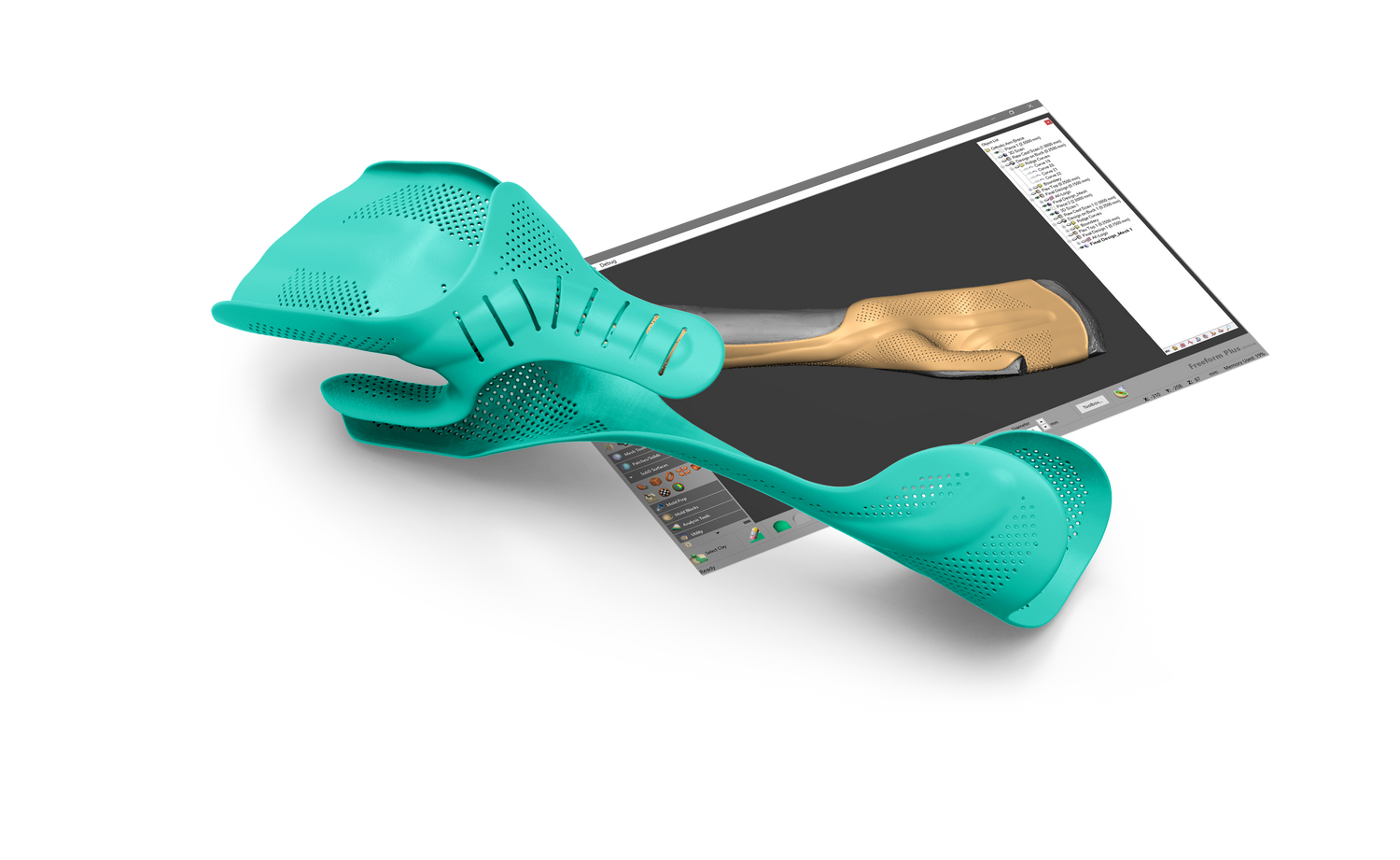

Free Form Modeling
Surface modeling is best used when creating a freeform or organic object. It is not parametric, meaning it doesn’t have a history tree and can be hard to make big changes. Surface modeling allows fluid construction or organic shapes by manipulating the surface to form an object. This also means the object is hollow inside until the engineer builds enough of the surfaces to “lock” the part.

Sculpting
As with the surface modeling, sculpting is used in creation of organic/freeform objects. The difference lies in the principle of the model construction: a specialist starts with a stimulated ball of clay and works on an object as a real sculptor. Sculpted meshes usually have millions of polygons, which makes them the “heaviest” 3D model.
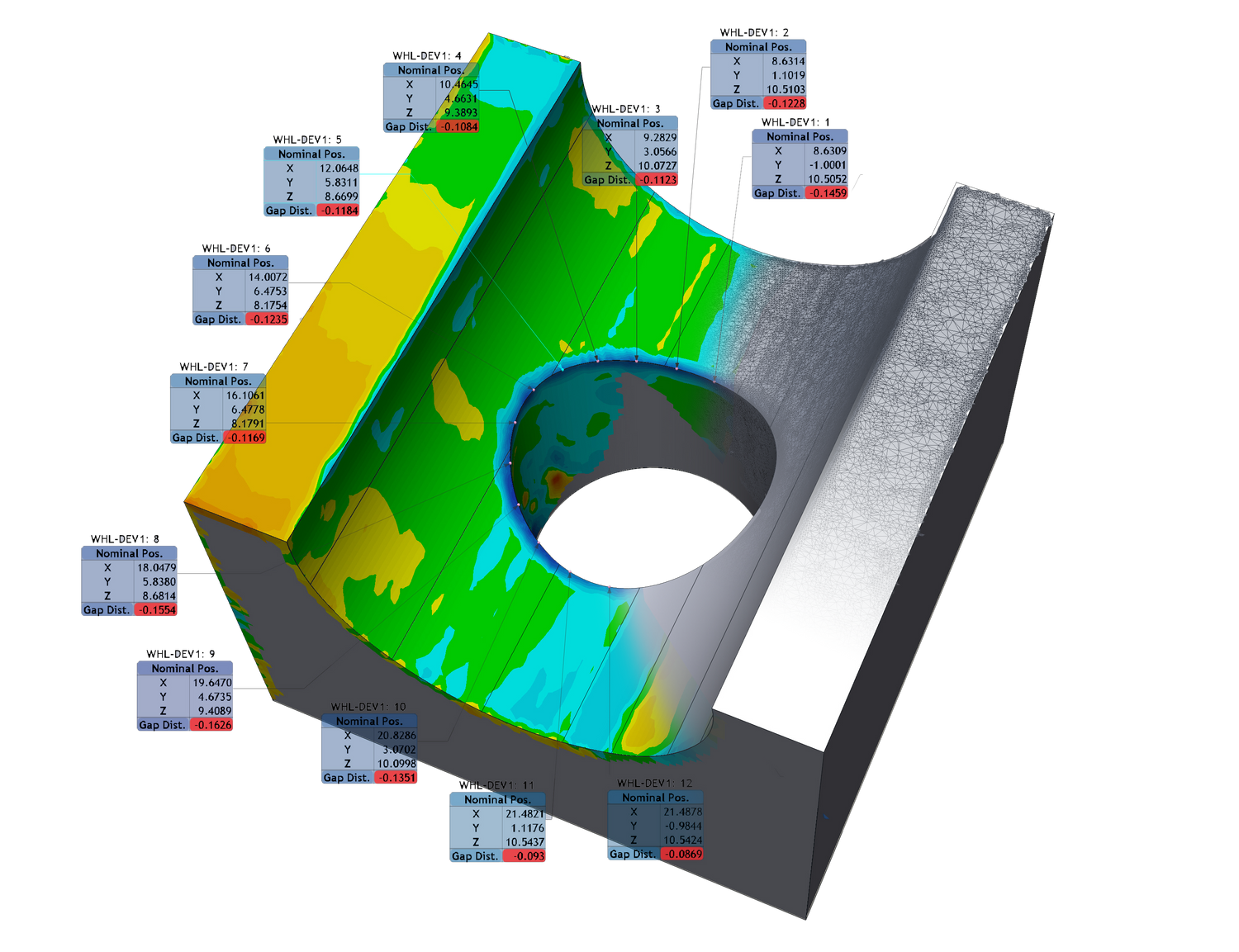
Inspection
3D scanners can replace traditional measurement tools for 2D and 3D complicated mechanical parts or organic shapes. Free software tools provides simple tools to annotate, extract distance (point to point), volume, and surface area from a 3D model. More sophisticated software can help creators measure parts of the body, objects for design purposes, quality control and inspection
Software Packages
Mesh-to-CAD of Mostly Mechanical Parts
Advanced-level software
Intermediate-level software
Geomagic for SolidWorks
SolidEdge Shining 3D Edition
Fusion 360 Commercial edition
Beginner-level software
Fusion 360 Free Edition
Mesh-to-CAD of Freeform shapes
Advanced-level software
Intermediate-level software
Geomagic Wrap
Rhinoceros 3D
Beginner-level software
Fusion 360 Both editions
Inspection and Quality Control
Free software
Beginner Software
Meshmixer - for Mesh-to-Sculpted Model
Meshlab - for Mesh-to-Sculpted Model
Cloud Compare - for Inspection and Quality Control
